
glass beads factory
The Art and Science of Glass Beads Manufacturing
Glass beads have captivated artisans, jewelers, and craftspeople for centuries, not merely for their aesthetic appeal but also for their versatility and durability. The process of manufacturing glass beads, from raw materials to the finished products, intertwines art and science, showcasing the intricate craftsmanship behind this seemingly simple object.
The Raw Materials
The journey of a glass bead begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials. The primary ingredient is silica, which is derived from sand. Depending on the desired characteristics of the final product, manufacturers often blend silica with various other materials. These additives can include soda ash, which lowers the melting point of the glass, and lime, which helps improve durability. Additionally, different metal oxides are incorporated to create various colors and effects. For example, cobalt oxide produces blue hues, while iron oxide can yield a range of greens and browns.
The Melting Process
Once the raw materials are prepared, the next step is melting. This process takes place in large furnaces that can reach temperatures exceeding 1,700 degrees Celsius. Here, the silica and additives are heated until they reach a molten state. Precise temperature control is vital, as slight variations can lead to inconsistencies in color and texture. Skilled workers continuously monitor the melting process to ensure an even consistency while removing any impurities that can affect the final quality of the beads.
Shaping the Beads
After reaching the desired molten state, the glass is shaped into beads. This can be done using several techniques, including lampworking, pressing, and pouring into molds. In lampworking, a glass rod is heated in front of a flame until it becomes pliable, allowing artisans to form intricate designs. Alternatively, for mass production, beads can be formed by pressing molten glass into molds, resulting in uniform shapes and sizes.
Surface Treatments
glass beads factory
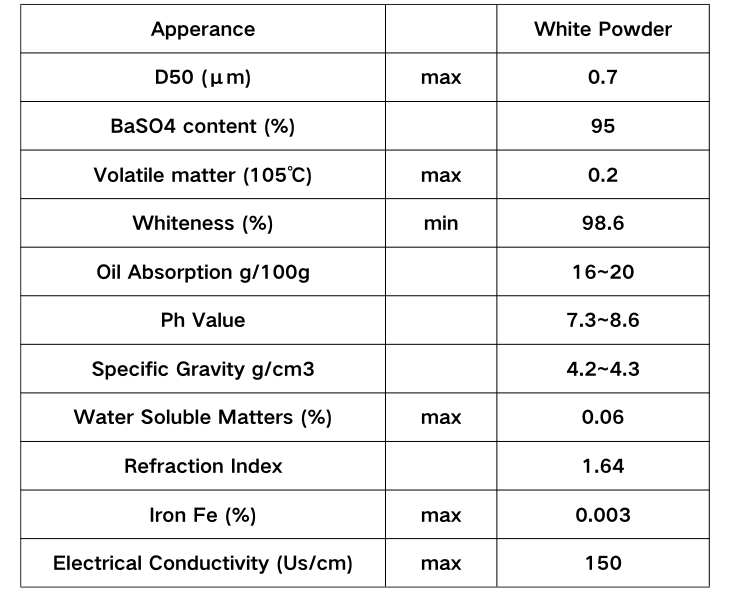
Once the beads are formed and cooled, they may undergo additional treatments to enhance their appearance. Polishing is a common technique used to give the beads a glossy finish, while etching or sandblasting can create a textured surface. Additionally, coatings may be applied to create unique visual effects, such as metallic finishes or iridescence.
Quality Control
Quality control is paramount in glass bead manufacturing. Each batch of beads undergoes rigorous inspection to ensure they meet the required standards for size, color, and finish. Advanced technologies, such as optical inspection systems, are employed to detect defects that may be invisible to the naked eye. This meticulous attention to detail ensures that only the highest quality beads are released to the market.
The Final Product
The final product—a vibrant array of glass beads—can be used in various applications, from jewelry making to decorative crafts. Their versatility allows artisans to explore endless design possibilities, whether creating intricate necklaces, chunky bracelets, or elaborate home decor items. The beads can be strung together, used as embellishments, or even incorporated into larger art pieces, showcasing the ingenuity of the creator.
Sustainability and Innovation
In recent years, the glass beads industry has also been embracing sustainability. Many manufacturers are incorporating recycled glass into their production processes, reducing the environmental impact of glass bead manufacturing. Innovations such as energy-efficient furnaces and eco-friendly packaging are becoming more commonplace, reflecting a growing commitment to environmentally responsible practices.
Conclusion
The process of manufacturing glass beads exemplifies a seamless blend of artistry and scientific precision. Each bead encapsulates not only the creative vision of the artisan but also the intricate processes that bring them to life. As trends evolve and consumer preferences shift, the glass bead industry continues to thrive, remaining a beloved medium for self-expression and creativity worldwide. Whether used in traditional jewelry or contemporary art, glass beads will undoubtedly continue to enchant for generations to come.
Share
-
Premium Resin Coated Sand - High Heat Resistance CastingNewsJul.31,2025
-
High Quality Silicon Carbide Grit for Abrasive ApplicationsNewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Quality Ceramsite for Plants & Gardening | Lightweight PebblesNewsJul.29,2025
-
Premium Burgundy Glass Marbles for Vases & Shooter GamesNewsJul.29,2025
-
High Purity Quartz Sand for Industrial and Ground ApplicationsNewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Quality Barite Powder for Drilling & Industrial UseNewsJul.29,2025






